Embark on an in-depth exploration of sensory profile 2 scoring interpretation, a comprehensive tool that unveils the complexities of sensory processing. This detailed guide provides a panoramic view of the assessment’s purpose, scoring system, and its profound implications for understanding sensory processing patterns, modulation, and environmental influences.
Delve into the intricacies of sensory processing patterns, unraveling the unique characteristics and behaviors associated with each type. Discover the significance of sensory modulation and its impact on daily functioning, gaining insights into the challenges faced by individuals with sensory processing difficulties.
Sensory Profile 2 Scoring Interpretation
The Sensory Profile 2 is a standardized assessment tool used to evaluate sensory processing abilities in individuals. It provides a comprehensive profile of an individual’s sensory processing patterns, strengths, and challenges.
The Sensory Profile 2 uses a four-point Likert scale to rate the frequency and intensity of sensory behaviors. The scoring system ranges from 0 (never) to 3 (always). The higher the score, the more frequently and intensely the sensory behavior is observed.
Sections and Subcategories, Sensory profile 2 scoring interpretation
The Sensory Profile 2 includes four sections:
- Sensory Processing
- Sensory Modulation
- Sensory Discrimination
- Sensory Motor
Each section is further divided into subcategories that assess specific aspects of sensory processing.
Sensory Processing Patterns: Sensory Profile 2 Scoring Interpretation
The Sensory Profile 2 identifies four primary sensory processing patterns:
- Sensory Modulation Disorder (SMD)
- Sensory Over-Responsivity (SOR)
- Sensory Under-Responsivity (SUR)
- Sensory Seeking
Characteristics and Behaviors
- SMD:Difficulty regulating sensory input, leading to over- or under-responsiveness to sensory stimuli.
- SOR:Exaggerated responses to sensory stimuli, resulting in avoidance or distress.
- SUR:Reduced responses to sensory stimuli, leading to a lack of awareness or engagement.
- Sensory Seeking:Craving for intense sensory experiences to compensate for low sensory awareness.
Sensory Modulation
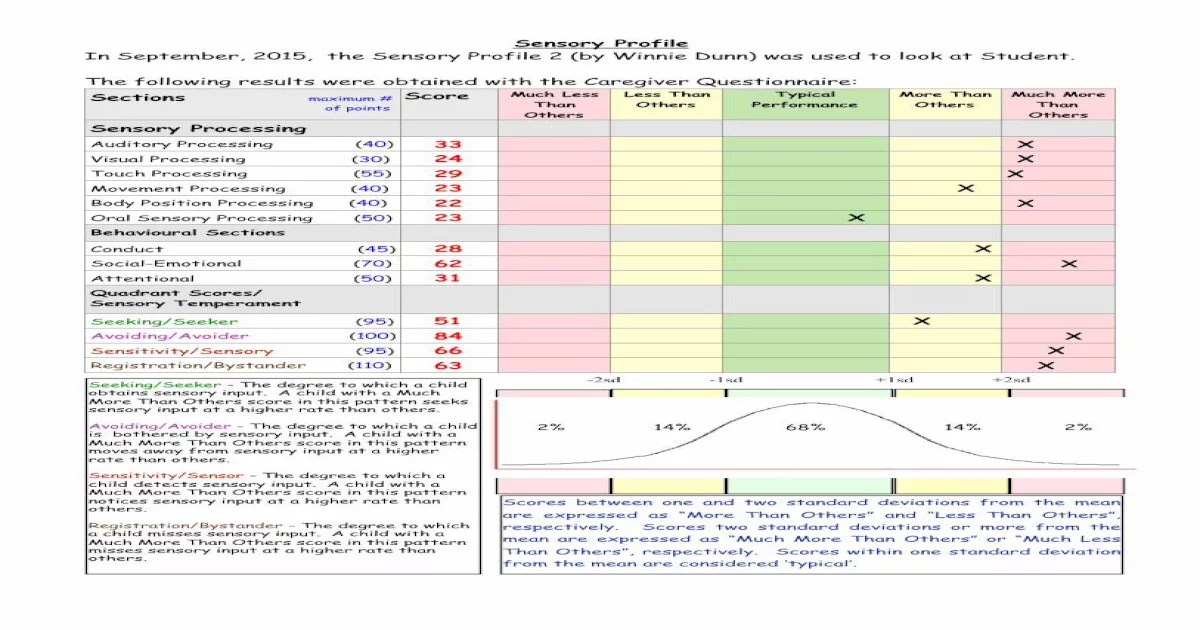
Sensory modulation refers to the brain’s ability to regulate and organize sensory input. Difficulties in sensory modulation can lead to sensory processing challenges.
Types of Difficulties
- Sensory Over-Responsivity:Difficulty filtering out sensory information, leading to overwhelming responses.
- Sensory Under-Responsivity:Difficulty detecting or responding to sensory stimuli, leading to a lack of awareness.
- Sensory Seeking:Craving for intense sensory experiences to compensate for low sensory awareness.
Impact on Behavior
Sensory modulation difficulties can affect behavior in various ways, including:
- Hyperactivity and impulsivity
- Withdrawal and avoidance
- Difficulty with attention and focus
- Social and emotional challenges
Sensory Environment

Creating a supportive sensory environment is crucial for individuals with sensory processing difficulties.
Modifying the Environment
- Reduce Sensory Input:Dimming lights, using noise-canceling headphones, or providing a quiet space.
- Increase Sensory Input:Providing bright lights, playing music, or using fidget toys.
- Control Sensory Stimulation:Offering a variety of sensory experiences, such as weighted blankets, tactile toys, or aromatherapy.
Sensory Diets and Interventions
Sensory diets and other interventions can help manage sensory processing challenges:
- Sensory Diets:Planned sequences of sensory activities designed to provide specific sensory input.
- Occupational Therapy:Therapeutic interventions that focus on improving sensory processing skills.
- Sensory Integration Therapy:A type of therapy that uses sensory experiences to improve sensory processing and behavior.
Intervention and Support

Various interventions are available for individuals with sensory processing difficulties.
Therapeutic Approaches
- Occupational Therapy:Focuses on improving sensory processing skills, motor coordination, and daily living skills.
- Sensory Integration Therapy:Uses sensory experiences to improve sensory processing and behavior.
- Speech-Language Therapy:Addresses communication difficulties related to sensory processing.
Interdisciplinary Collaboration
Interdisciplinary collaboration is essential for providing comprehensive support:
- Occupational Therapists:Assess and treat sensory processing difficulties.
- Speech-Language Pathologists:Address communication challenges.
- Physical Therapists:Improve motor coordination and balance.
- Psychologists:Provide emotional and behavioral support.
Case Studies and Examples
| Case Study | Sensory Processing Pattern | Intervention | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Child A | Sensory Over-Responsivity | Sensory integration therapy, weighted blanket | Improved sensory regulation, reduced hyperactivity |
| Child B | Sensory Under-Responsivity | Sensory diet, fidget toys | Increased sensory awareness, improved attention |
| Child C | Sensory Seeking | Occupational therapy, sensory room | Reduced craving for intense sensory experiences, improved social skills |
Query Resolution
What is the purpose of sensory profile 2 scoring interpretation?
Sensory profile 2 scoring interpretation aids in identifying sensory processing patterns, modulation difficulties, and environmental influences that impact an individual’s daily functioning.
How does sensory modulation affect behavior?
Sensory modulation difficulties can manifest in various behaviors, including hyperactivity, impulsivity, withdrawal, and difficulty regulating emotions.
What is the role of sensory diets in managing sensory processing challenges?
Sensory diets provide structured sensory experiences that aim to regulate sensory processing and improve daily functioning.